Introduction
The maximum value (g mo) is specified in particular Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) data sheet. It is usually present in the units of conductance in particularly by unit Siemens. For FET, the standard values of Transconductance (gm) are in range of one to thirty milli siemens. AC Drain Resistance, (rd). Following are some important points to remember about FET − Gate − By using diffusion or alloying technique, both sides of N type bar are heavily doped to create PN junction. These doped regions are called gate.
Further Education and Training (FET) training courses are provided in Education and TrainingBoard (ETB) Training Centres. If you are unemployed or redundant or if youwish to update your skills or change your career, there is a wide range oftraining courses available to assist you.
You are eligible to take part in a FET training course if you areunemployed, redundant or no longer in full-time education. You may also beeligible if you are getting a disability-related social welfare payment or aOne-Parent Family Payment.
FÁS, SOLAS and ETBs
FÁS was dissolved and some of its functions were transferred to SOLAS - the new further education and trainingauthority.
FET and COVID-19
Further and higher education institutions across Ireland have introducedenhanced public health measures. Colleges will use remote learning wherepossible and minimise on-site activities. You can check your college’sarrangements during COVID-19.
Echelon port devices driver download for windows 10. eCollege is temporarily offering itscourses free of charge in digital, ICT and business skills with certificationif you have been affected by COVID-19 restriction measures.
You can apply if you are aged over 18 and you are already doing a FETcourse. You can also apply if you have recently become unemployed or had yourhours cut due to COVID-19 restrictions.
Types of training courses
G Fet
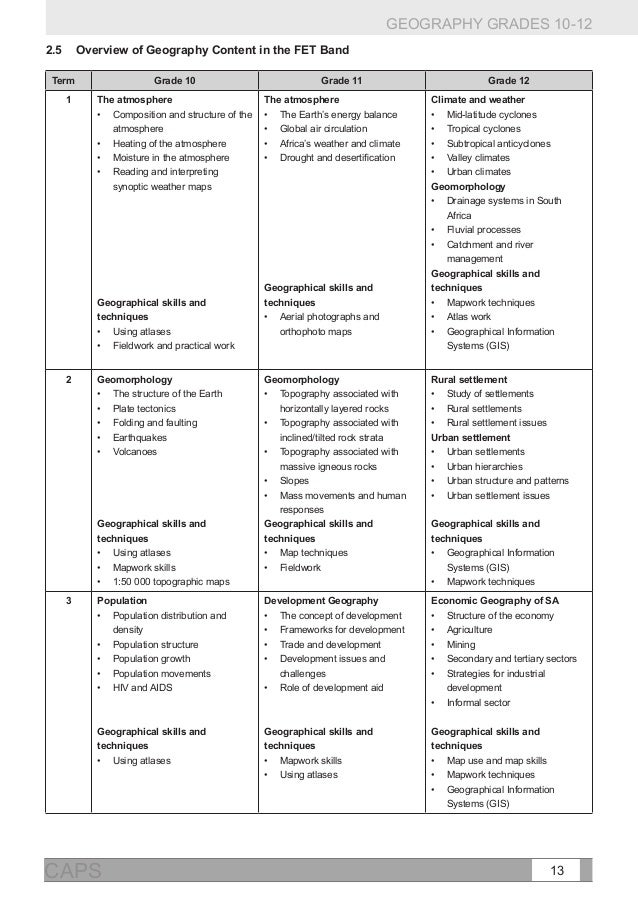
There are training courses available under 2 different types of training.
TheTraineeship Programme provides training and relevant workexperience. If you are unemployed and looking for an opportunity to gaintraining, experience and a formal qualification in a particular area of work,the Traineeship Programme may suit your needs. Traineeships are full-time. Theduration of the programme will depend on the area in which you choose to train.When your initial training is completed, you move back and forth between thecentre and the employer's workplace, further developing your skills and gainingpractical experience. When you complete your course you will receive aQualification and Quality Ireland (QQI) award at either Certificate or AdvancedCertificate level.
The range oftraineeships available is likely to change so you need to keep in touchwith your local employment services office or Intreo centre for up-to-dateinformation.
Specific SkillsTraining allows people who have lost their job or who are changingjob to learn new job-related skills. There are short and long day courses,online courses, blended learning and evening courses.The courses on offervary from centre to centre and from year to year with different levels ofcertification. The courses are run during the day and in the evenings. Priorityon daytime courses is given to unemployed people. A day course is free to allunemployed people, even if you are not getting a social welfare payment. Anevening course is not free unless you are getting a social welfare payment.
Rates
Further Education and Training (FET) training allowances
A FET training allowance may be paid if you take part in theTraineeship Programme or Specific SkillsTraining.
Apart from evening courses, all FET training courses are free and you may bepaid a FET trainingallowance for the duration of your course. You can also claim a mealallowance, an accommodationallowance if you need to live away from home for the duration of the courseor a travelallowance if you live 5 km or more from the course centre. You may alsoqualify for freechildcare.
You can read more details in our document on FET trainingallowances.
Drivers leadership laptops & desktops.
How to apply
To apply for a place on a FETtraining course, you should register with your localemployment services office or Intreocentre. You will be interviewed to identify the course that will best suityour needs. Due to the pressure on some courses, you may not get a placeimmediately on the course of your choice. For more information about availabletraining courses contact your ETB TrainingCentre.
- Semiconductor Devices Tutorial
- Semiconductor Devices Resources
- Selected Reading
A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a three-terminal semiconductor device. Its operation is based on a controlled input voltage. By appearance JFET and bipolar transistors are very similar. However, BJT is a current controlled device and JFET is controlled by input voltage. Most commonly two types of FETs are available.
- Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (IGFET)
Junction Field Effect Transistor
The functioning of Junction Field Effect Transistor depends upon the flow of majority carriers (electrons or holes) only. Basically, JFETs consist of an N type or P type silicon bar containing PN junctions at the sides. Following are some important points to remember about FET −
Gate − By using diffusion or alloying technique, both sides of N type bar are heavily doped to create PN junction. These doped regions are called gate (G).
Source − It is the entry point for majority carriers through which they enter into the semiconductor bar.
Drain − It is the exit point for majority carriers through which they leave the semiconductor bar.
Channel − It is the area of N type material through which majority carriers pass from the source to drain.
There are two types of JFETs commonly used in the field semiconductor devices: N-Channel JFET and P-Channel JFET.
N-Channel JFET
It has a thin layer of N type material formed on P type substrate. Following figure shows the crystal structure and schematic symbol of an N-channel JFET. Then the gate is formed on top of the N channel with P type material. At the end of the channel and the gate, lead wires are attached and the substrate has no connection.
When a DC voltage source is connected to the source and the drain leads of a JFET, maximum current will flow through the channel. The same amount of current will flow from the source and the drain terminals. The amount of channel current flow will be determined by the value of VDD and the internal resistance of the channel.
A typical value of source-drain resistance of a JFET is quite a few hundred ohms. It is clear that even when the gate is open full current conduction will take place in the channel. Essentially, the amount of bias voltage applied at ID, controls the flow of current carriers passing through the channel of a JFET. With a small change in gate voltage, JFET can be controlled anywhere between full conduction and cutoff state.
P-Channel JFETs
It has a thin layer of P type material formed on N type substrate. The following figure shows the crystal structure and schematic symbol of an N-channel JFET. The gate is formed on top of the P channel with N type material. At the end of the channel and the gate, lead wires are attached. Rest of the construction details are similar to that of N- channel JFET.
Normally for general operation, the gate terminal is made positive with respect to the source terminal. The size of the P-N junction depletion layer depends upon fluctuations in the values of reverse biased gate voltage. With a small change in gate voltage, JFET can be controlled anywhere between full conduction and cutoff state.
Output Characteristics of JFET
The output characteristics of JFET are drawn between drain current (ID) and drain source voltage (VDS) at constant gate source voltage (VGS) as shown in the following figure.
Initially, the drain current (ID) rises rapidly with drain source voltage (VDS) however suddenly becomes constant at a voltage known as pinch-off voltage (VP). Above pinch-off voltage, the channel width becomes so narrow that it allows very small drain current to pass through it. Therefore, drain current (ID) remains constant above pinch-off voltage.

Parameters of JFET
The main parameters of JFET are −
- AC drain resistance (Rd)
- Transconductance
- Amplification factor
AC drain resistance (Rd) − It is the ratio of change in the drain source voltage (ΔVDS) to the change in drain current (ΔID Audiotrak products driver download for windows 10. ) at constant gate-source voltage. It can be expressed as,
Rd = (ΔVDS)/(ΔID) at Constant VGS
Transconductance (gfs) − It is the ratio of change in drain current (ΔID) to the change in gate source voltage (ΔVGS) at constant drain-source voltage. It can be expressed as,
Get Epic
gfs = (ΔID)/(ΔVGS) at constant VDS
Amplification Factor (u) − It is the ratio of change in drain-source voltage (ΔVDS) to the change in gate source voltage (ΔVGS) constant drain current (ΔID). It can be expressed as,
u = (ΔVDS)/(ΔVGS) at constant ID
